Cloud-Native Architecture and Kubernetes
Driving Digital Transformation
In the current digital landscape, businesses constantly seek new ways to innovate and stay ahead of the competition. Cloud-native architecture and Kubernetes have emerged as two powerful tools for achieving this goal. Cloud technology provides a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective way to store and access data, while Kubernetes enables the seamless orchestration and management of containerized applications. These technologies enable businesses to adapt quickly to changing market demands and stay agile and responsive in an ever-evolving business landscape. This article delves into the core concepts of cloud and Kubernetes, showcasing how they work together to drive innovation and transformation in modern businesses.
Cloud-Native Architecture
Cloud-native architecture refers to designing and implementing applications that leverage cloud services and infrastructure to deliver high performance and reliability. By breaking monolithic applications into smaller, loosely coupled microservices, organizations can achieve greater scalability and resilience in their systems.
Benefits of Cloud-Native Architecture:
Scalability: Cloud-native applications can seamlessly scale up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance at all times.
Flexibility: Microservices' modular nature allows for rapid development and deployment, enabling teams to respond quickly to changing market conditions.
Resilience: Cloud-native applications are inherently more resilient to failures and downtime because they distribute workloads across multiple containers and nodes.
Kubernetes
Kubernetes is an open-source platform that provides container orchestration capabilities. It easily enables the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Kubernetes automates essential tasks such as load balancing, scaling, and resource allocation, empowering organizations to develop and run cloud-native applications efficiently. With its advanced features, Kubernetes makes it easy to manage complex containerized environments and ensures that applications run reliably, securely, and at scale.
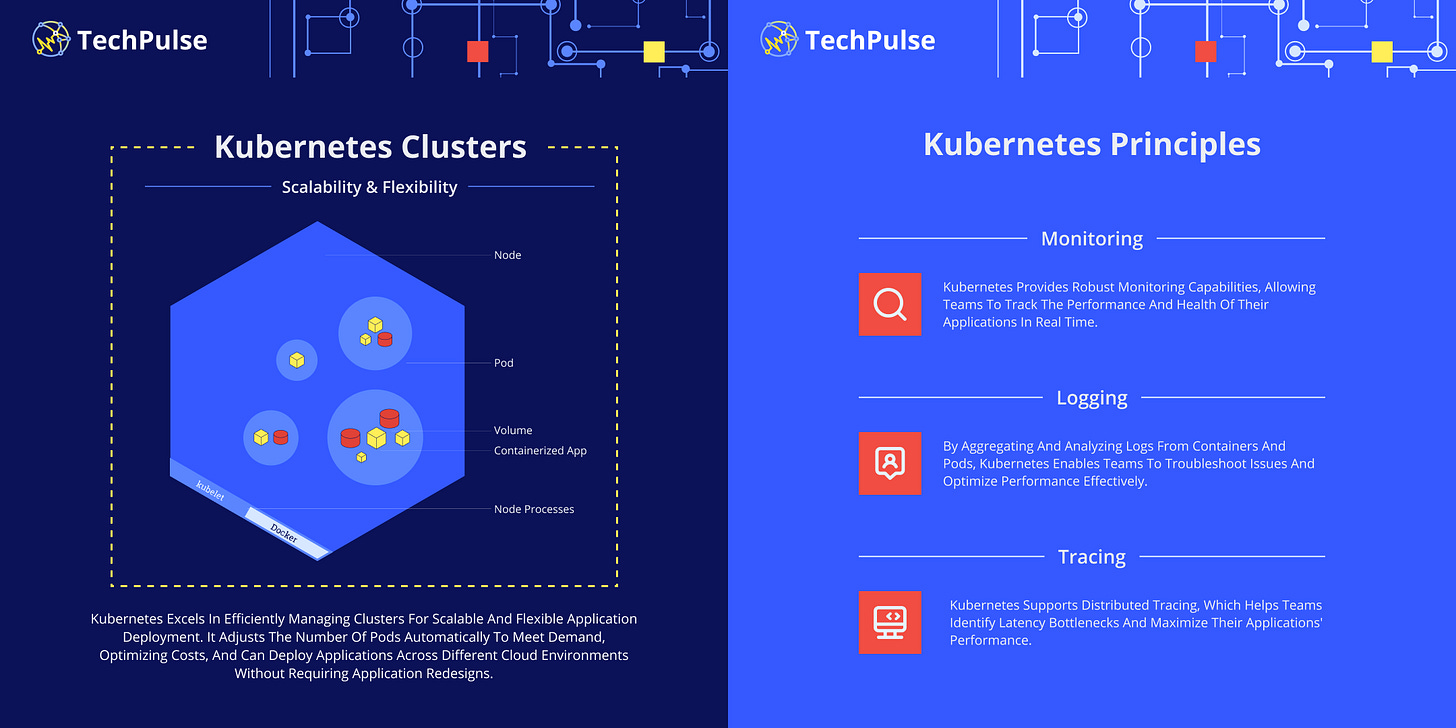
Kubernetes Observability Principles:
Monitoring: Kubernetes provides robust monitoring capabilities, allowing teams to track the performance and health of their applications in real time.
Logging: By aggregating and analyzing logs from containers and pods, Kubernetes enables teams to troubleshoot issues and optimize performance effectively.
Tracing: Kubernetes supports distributed tracing, which helps teams identify latency bottlenecks and maximize their applications' performance.
Visual Representation
To better understand the concepts discussed, let's explore some visual representations:
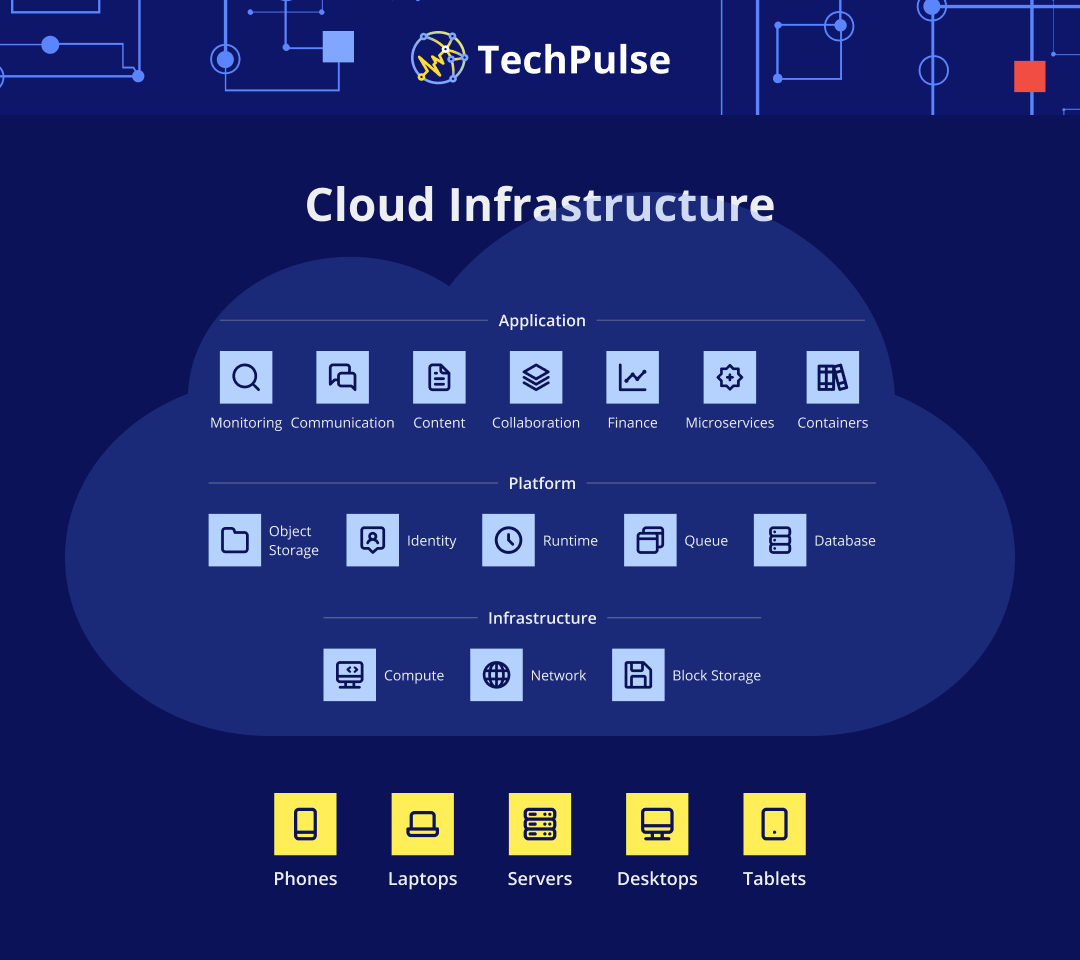
Key components of cloud-native architecture, including microservices, containers, and cloud infrastructure.
Kubernetes observability principles and clusters scalability and flexibility benefits:
By embracing cloud-native architecture and Kubernetes technologies, organizations can greatly improve their growth, innovation, and competitiveness. With cloud-native architecture, organizations can construct and distribute highly scalable and robust applications, while Kubernetes provides orchestration and automation capabilities for efficient application management. These tools offer a comprehensive solution for organizations to streamline their operations, reduce expenses, and enhance their overall performance.
Stay tuned for more insights on cloud-native technologies and digital transformation strategies.